- Huangshan UNESCO Global Geopark
- Naturtejo UNESCO Global Geopark, Portugal
- Central Catalonia UNESCO Global Geopark, Spain
- Jiuhuashan UNESCO Global Geopark
- Yandangshan UNESCO Global Geopark
- Sanqingshan UNESCO Global Geopark
- Longhushan UNESCO Global Geopark
- Terra Vita UNESCO Global Geopark, Germany
- Huanggang Dabieshan UNESCO Global Geopark
- Fangshan UNESCO Global Geopark
- English Riviera UNESCO Global Geopark
- Guangwushan-Nuoshuihe UNESCO Global Geopark
- Zhijingdong Cave UNESCO Global Geopark
- Dali-Cangshan UNESCO Global Geopark
- Xiangxi UNESCO Global Geopark
- Yuntaishan UNESCO Global Geopark
- Linxia UNESCO Global Geopark
- Kanbula UNESCO Global Geopark
- Wudalianchi UNESCO Global Geopark
- Changbaishan UNESCO Global Geopark
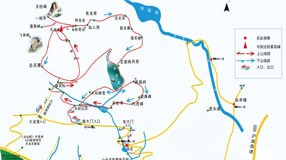
Yandangshan UNESCO Global Geopark is located in the cities of Wenzhou and Taizhou in Zhejiang Province. It comprises Yandangshan, Nanxijiang, Fangshan – Changyu Dongtian (Changyu Cave) with a total area of 298.80 km2. It is dominated by volcanic geology and landscape, interacting with religious history, cultural landscape and stone culture to form a comprehensive nature park. The park was approved as a national park in 1982, a member of the Global Geoparks Network in 2005 and one of the first 5A National Scenic Attractions in 2007.
Yandangshan is one of the most famous ‘three hills and five mountains’ of China. It is located at the western end of the Asia Pacific continental margin. It is a gigantic ancient volcano with global representation and significance in terms of the different types of volcanic rocks and landforms. About 140 million years ago, the Paleo-Pacific Plate subducted beneath the continental plate to create a large-scale volcanic and magmatic intrusion on the edge of the continental plate. Yandangshan experienced four stages of volcanic eruption and underwent tremendous geological transformation to form today's towering peaks, peculiar rocks and waterfalls. The geology and natural landscape have recorded the evolution of the ancient volcano, revealing the mystery of its eruption and changes more than 100 million years ago.