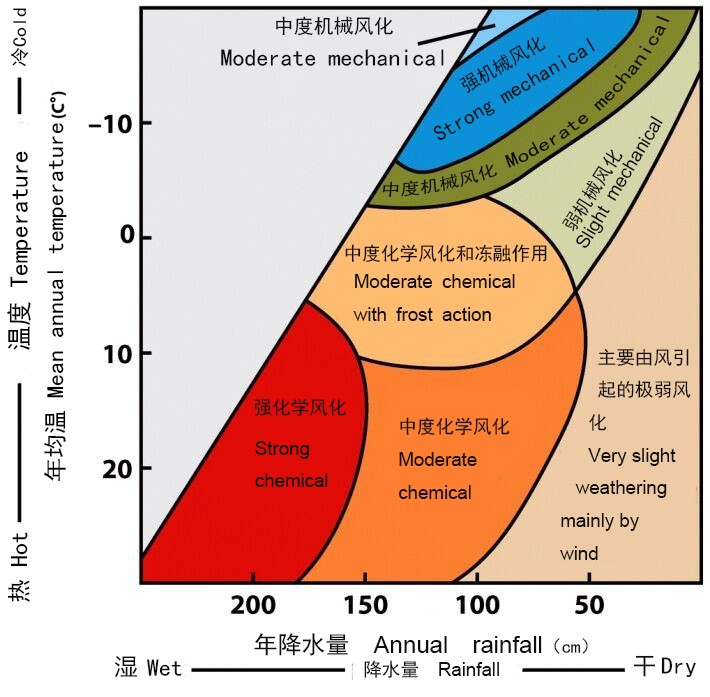
Climate
Climate is a key factor that
determines the rate of weathering of granite through different temperatures and
rainfall.
Did you know?
In Tianzhushan area, the annual
rainfall is 190cm and the mean annual temperature is 9.5℃.
Which kind of weathering is there?
Temperature’s effect on granite
1.Fall in temperature makes the water
in joints or fractures freeze . With its volume expanding, the force generated
in this process leads to the expansion of the fractures, which contributes to
the collapse and cracking of the granite.
2.The granite is composed of minerals
with different expansion rates. The temperature difference between day and
night causes the expansion of the spacing among mineral grains, making the
surface and interior of the granite crack and peel off, which is conducive to
weathering.
3.Chemical and biochemical weathering
are stronger in warm and humid climates. Minerals composing granite, such as
feldspar and mica are prone to be broken down chemically into clay minerals.
Rock composition
The weathering resistances of
different rocks or minerals are not the same; therefore rocks are weathered at
different rates and intensity, which contributes to the formation of peculiar
peaks and rocks.
.jpg)
Granite is composed of quartz,
potassium feldspar, plagioclase, biotite, hornblende and so on.
Weathering resistance: quartz>potassium
feldspar & plagioclase>biotite & hornblende
Rock texture
The density and the size of the
particles of the rock may have the weathering resistance of the rock. Rocks
with loose texture or composed of particles with varied sizes are prone to
weathering. Rocks with coarse particles are more easily weathered compared to
those with fine particles.
Rock structure rocks with joints or
fractures are exposed to weathering factors (such as water, plant roots),
facilitating the weathering process.
As a rock is reduced into smaller and
smaller particles, its surface area increases but its volume remains the same.