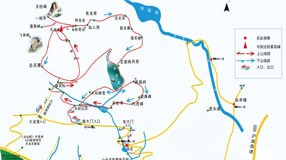
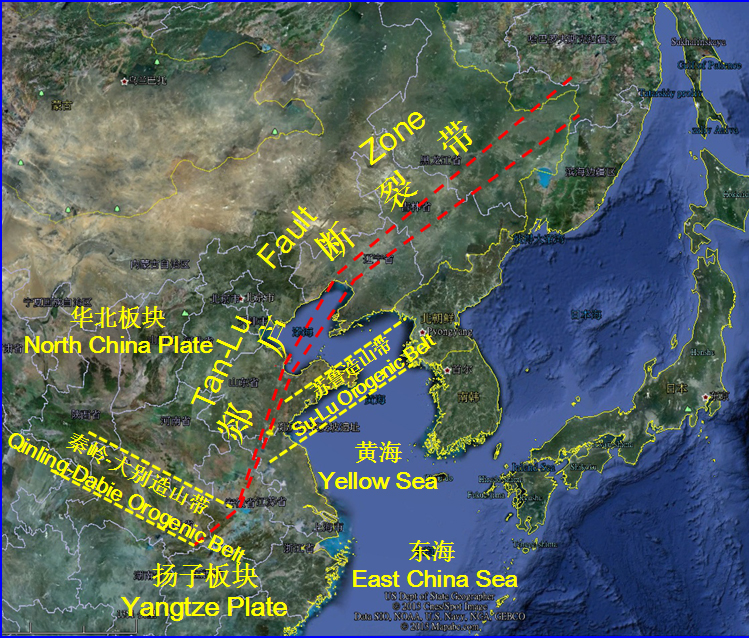
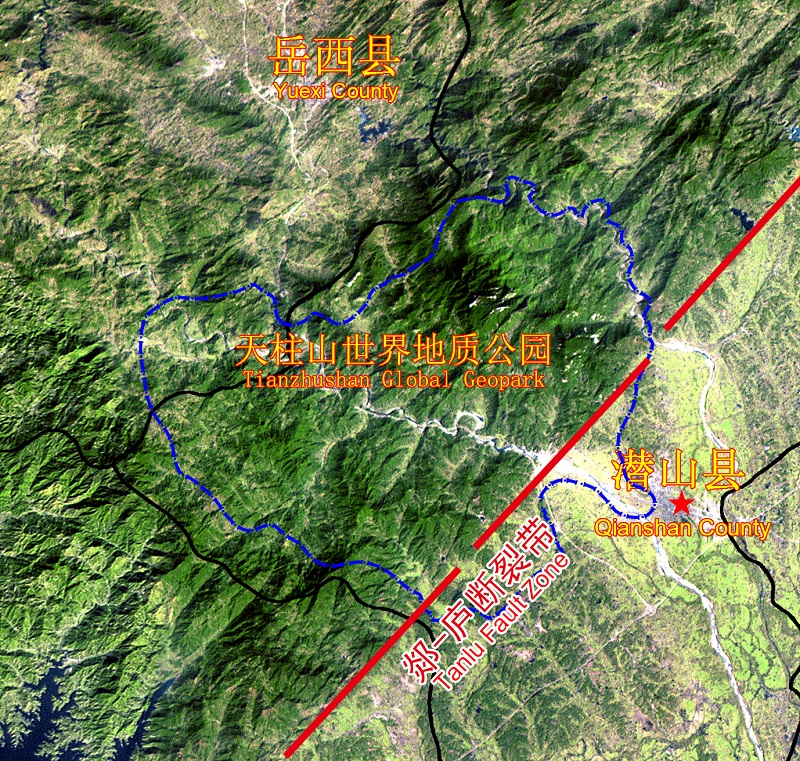
Tan-Lu fault is the main fault zone
on the East-Asia continent. Over 2400km of it is within the Chinese border and has cut
through different tectonic units of eastern China. It forms the boundary
line between the UHP metamorphic belt of Dabie Mountain and the Qianshan Basin,
which also divides the high mountain and basin in terms of landform. It has
also played an important role in the folding back of the UHP metamorphic belt
of Dabie Mountain and the formation of the magnificent granite landform in
Tianzhu Mountain.
Do you know what a fault is?
The stratum may fracture under
certain stress and if the rocks on either side of the fracture have moved past
each other, it is called a fault. Fault on a large scale is referred to as a fault
zone. The fault plane is where the rock breaks and moves. The rock above the
fault plane is called the hanging wall, and the one beneath the fault plane is the footwall. According to their movements along fault planes, faults can be divided
into normal faults, reverse faults and Strike-Split fault.
Normal fault: the hanging wall moves
downward and footwall moves upward.
Reverse fault: hanging wall rises and
the footwall descends.
Strike-split fault: rocks move
horizontally along the fault plane.