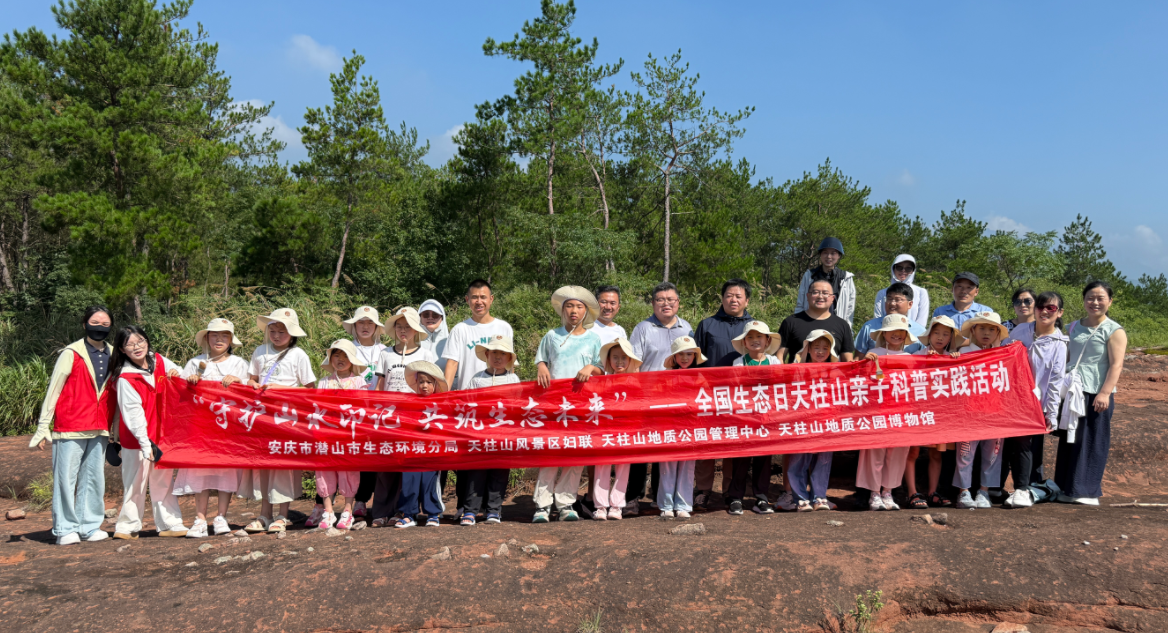
Do you know what a fault is?
Category:Science Popularization
The stratum may fracture under
certain stress and if the rocks on either side of the fracture have moved past
each other, it is called a fault. A fault on a large scale is referred to as a fault
zone. The fault plane is where the rock breaks and moves. The rock above the
fault plane is called a hanging wall, and the one beneath the fault plane is a footwall. According to their movements along the fault plane, faults can be divided
into normal faults, reverse faults and Strike-Split faults.